CuproBraze heat exchangers are made using special anneal-resistant alloys of copper and brass. Tubes are fabricated from brass strip and coated with a brazing filler material. The copper fins, coated tubes, headers and side-supports made of brass are fitted together into a core assembly, which is then brazed in a furnace.
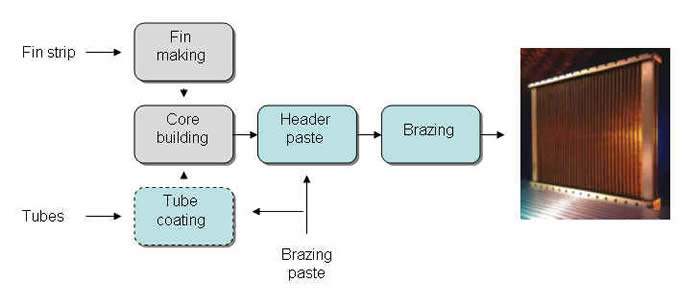
Many small, mid-size and high-volume production facilities are making CuproBraze heat exchangers for OEMs and the aftermarket since year 2000. So called one-shot brazing entered production scale in 2008.
CuproBraze technology is flexible and scalable. The International Copper Association licenses CuproBraze technology free of charge to heat exchanger manufacturers. Technical experts of the member companies of CuproBraze Alliance will assist you in transferring the technology to your production line anywhere in the world.
Tubes -Start with the Tubes
Process description

The most common method for making tubes is HF-welding. Special machinery forms the brass strip into tubes. The edges of the strip are then welded together and the welded tube cut to length in the same machine. Welded CuproBraze tubes can also be purchased.
A typical radiator tube has cross sectional dimensions of about 16 x 2 mm and wall thickness 118 to 152 µm, depending on application.
The external surfaces of both the radiator tubes and CAC tubes are then sprayed with brazing paste and dried.

Charge air cooler tubes are bigger. The cross sectional area is typically 60 x 6 mm and wall thickness 200 µm. In addition, internal turbulators formed of copper strip are inserted, together with brazing foil, which forms the joints between the turbulators and the inner walls of the tubes during brazing CAC tube with inner turbulators. Brazing foil inserted between the turbulators and inner tube wall.
High or medium volume



Low volume
 For low volume production it makes sense to buy tubes. Tube coating can be done manually with a simple HVLP-spraygun. The tubes are dried with warm air blowing.
For low volume production it makes sense to buy tubes. Tube coating can be done manually with a simple HVLP-spraygun. The tubes are dried with warm air blowing.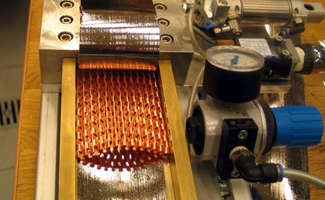 A simple tool can be used for inserting turbulators and the brazing foil into the CAC tubes.
A simple tool can be used for inserting turbulators and the brazing foil into the CAC tubes.Fins- Bring in the Fins
Process description
Copper fins are essential to the operation of advanced heat exchangers. Their high thermal conductivity and great strength allow for the fabrication of much thinner fins than aluminum. A variety of fin designs can be fabricated depending on the application. The fins are cut to length and collected for assembly. The fin thicknesses start from 32 µm.
High or medium volume
 Fin machine
Fin machineLow volume
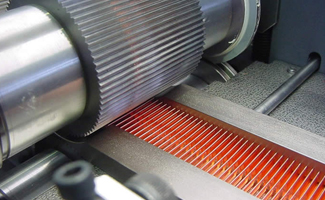 Fin machine is needed for all volumes of production.
Fin machine is needed for all volumes of production.Next Step Is Core Assembly
Process description
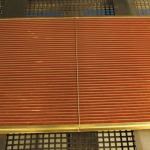
Typically, a heat-exchanger core is made from fins, tubes, header plates and side supports. Folded fins are inserted between the tubes.
The tube ends of the tube-fin assemblies must be inserted into holes in the header plates. These plates hold the entire assembly together.
High or medium volume
 A semi-automatic core builder
A semi-automatic core builderLow volume
 Core building table
Core building tableHeader Paste Application
Process description
A crucial step in the entire manufacturing process is the application of the brazing paste around the holes in the header plates. The quality of the tube-to-header joint plays a pivotal role in the longevity of the heat exchangers.
A long service life depends on uniform coverage of the joint on the header plate with the paste that contains the brazing alloy.
High or medium volume
 Header paste application machine
Header paste application machineLow volume
 Header paste can be applied manually simply from a squeeze bottle and dried with warm air blowing.
Header paste can be applied manually simply from a squeeze bottle and dried with warm air blowing.Brazing Furnace
Process description
The heart of the CuproBraze production line is the furnace. This is where heat-exchanger cores are brazed in a nitrogen atmosphere.
There are several types and sizes of furnaces available, depending on the part sizes and volume of production.
A CuproBraze brazing furnace is fitted with a forced nitrogen convection-cooling section to cool the parts to 150°C. Nitrogen convection cooling gives the product a bright appearance and allows the overall length of the furnace to be shorter.
High or medium volume
 A three-chamber furnace with a double in-out operating mode is ideal for a medium-size production line and increases productivity because it allows for more efficient use of the middle (brazing) chamber, where the holding time is the shortest.
A three-chamber furnace with a double in-out operating mode is ideal for a medium-size production line and increases productivity because it allows for more efficient use of the middle (brazing) chamber, where the holding time is the shortest.
For high-volume production, the best choice is a continuous furnace, in which heat exchangers are loaded onto a moving belt.
A typical high-volume production furnace is sized for brazing at rates of 1500 kg/h with a 1200 mm wide belt and a 350 mm pass height throughout the furnace. An automated control system allows for flexibility when brazing parts of different configuration and mass.
Low volume
 A single chamber batch furnace meets the needs of a small production volume
A single chamber batch furnace meets the needs of a small production volumeCuproBraze is Flexible and Scalable
A major advantage of the CuproBraze process is its flexibility. A wide variety of products can be processed on the same production line.
A worldwide network of materials suppliers and equipment makers stands ready to guide you, whether you plan to build a high-volume CuproBraze production facility or purchase CuproBraze heat exchangers from an Alliance member. For more detailed information about the CuproBraze process and the key factors for good results, please download the CuproBraze Brazing Handbook.
Key Factors for Good Results
- Use clean parts.
- Apply correct amount of filler metal.
- Do not overheat paste during drying.
- Use suitable fixturing during brazing.
- Check that the oxygen content is less than 20 ppm in the furnace.
- Apply correct brazing temperature on the parts
The contents of these items are explained in more details in the Handbook.

